Disappearing Hospitals, Where Did They Go? Woman’s Hospital
 The Woman’s Hospital, often considered the first hospital in this country dedicated to treating the diseases of women, opened on May 4, 1855 in a house on Madison Avenue. It was founded by the currently controversial J. Marion Sims, MD, pictured right, in concert with a group of influential New York City women. Sims arrived in New York in 1853 from his home in Alabama, where he developed a procedure to close vesicovaginal fistulas. He relocated to New York in hopes of improving his own chronic health condition.
The Woman’s Hospital, often considered the first hospital in this country dedicated to treating the diseases of women, opened on May 4, 1855 in a house on Madison Avenue. It was founded by the currently controversial J. Marion Sims, MD, pictured right, in concert with a group of influential New York City women. Sims arrived in New York in 1853 from his home in Alabama, where he developed a procedure to close vesicovaginal fistulas. He relocated to New York in hopes of improving his own chronic health condition.
At first, Sims was welcomed into the medical community of New York and invited to demonstrate his fistula procedure. Unfortunately, once local doctors learned the procedure, they lost interest in him. Sims was unable to establish a strong practice or find a hospital that would offer him operating privileges.
The wife of one of Sims’ few medical friends in the city offered to gather a group of interested and influential women to discuss the state of women’s health care in the city. Thirty-Five women met on February 6, 1855, the outcome of which was the establishment of the Woman’s Hospital Association. The group would move to establish and direct a hospital devoted to the reception and cure of women suffering from “diseases peculiar to their sex.” The Association set up a Board of Managers, referred to as the ‘Board of Lady Managers,’ comprised of thirty-five women, to guide the Hospital. An Executive Committee of seven women, appointed by the Board of Managers, managed the day-to-day affairs of the institution.
In 1857 the Hospital was re-incorporated by the New York State Legislature as the Woman’s Hospital in the State of New York, and re-organized under an all-male Board of Governors. The twenty-seven Governors were responsible for the overall concerns of the Hospital, including filling vacancies of non-female staff, enacting the By-Laws and organizing the Medical Department. Women, however, were still very much in charge of running the Hospital. The former Board of Lady Managers became the Board of Lady Supervisors, and managed the operations of the Hospital, including the appointment of nurses and other female attendants. A smaller Board of Lady Managers remained responsible for handling the day-to-day business of the Hospital. By 1887, the Board of Governors invited four women from the Board of Lady Supervisors to join them. They found this integration “to be most acceptable in its results,” and soon after the Board of Governors was reorganized and evenly divided between men and women.
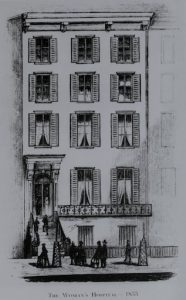 As mentioned above, the first Woman’s Hospital was a rented four-story brownstone at 83 Madison Avenue, off 29th Street, pictured left. The brownstone held forty beds and welcomed its first patient in May of 1855. The response to the Hospital’s opening was so great, by fall of 1855 that another surgeon, Thomas Addis Emmet, joined Dr. Sims as the second surgeon on staff. It wasn’t long before the Woman’s Hospital Board was seeking larger accommodations to meet patient demand.
As mentioned above, the first Woman’s Hospital was a rented four-story brownstone at 83 Madison Avenue, off 29th Street, pictured left. The brownstone held forty beds and welcomed its first patient in May of 1855. The response to the Hospital’s opening was so great, by fall of 1855 that another surgeon, Thomas Addis Emmet, joined Dr. Sims as the second surgeon on staff. It wasn’t long before the Woman’s Hospital Board was seeking larger accommodations to meet patient demand.
In 1858, approving the petition of Dr. Sims, the City of New York offered the entire block bounded by 49th and 50th Streets between Lexington and Park Avenues as a site for a new, larger hospital. Originally a Potter’s Field, or Stranger’s Burial Place, the plot was filled with coffins; more than 35,000 of them had to be removed. The first building, the Wetmore Pavilion, opened in 1867 and held seventy-five beds. A matching building, the Baldwin Pavilion, added in 1877, doubled that number. A Mr. Baldwin, who wished to remain anonymous, funded the construction of the second pavilion, contributing $84,000, provided the Association raised the balance of $50,000 to complete it.
 Over the years, the Board recognized the need to develop additional services. A post-graduate school of nursing admitted its first class in 1888. The establishment of a hospital pharmacy in 1881, a maternity ward in 1910, and a social services department in 1912 are examples of the additional services made available at Woman’s Hospital.
Over the years, the Board recognized the need to develop additional services. A post-graduate school of nursing admitted its first class in 1888. The establishment of a hospital pharmacy in 1881, a maternity ward in 1910, and a social services department in 1912 are examples of the additional services made available at Woman’s Hospital.
The 49th Street location proved to be an unsatisfactory one, as the ground tended to be wet, and the basement and ground floors had leaks and dampness. In 1902, all hospital services, except the Out-Patient Clinic, were suspended and the facility was sold. (On a side note, the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel opened on this same plot in 1931.)
 Hospital services resumed in 1906, when a newly constructed Woman’s Hospital opened on West 109th Street, between Amsterdam and Columbus Avenues, pictured left. The hospital functioned here until 1965, when it moved just a few blocks north into a newly constructed building on the St. Luke’s Hospital campus at Amsterdam Avenue at 114th Street, pictured right.
Hospital services resumed in 1906, when a newly constructed Woman’s Hospital opened on West 109th Street, between Amsterdam and Columbus Avenues, pictured left. The hospital functioned here until 1965, when it moved just a few blocks north into a newly constructed building on the St. Luke’s Hospital campus at Amsterdam Avenue at 114th Street, pictured right.
In 1952, realizing that their histories and ideals were parallel, and that it would be beneficial to each to consolidate their resources, which would also strengthen medical services offered to the broader Morningside Heights community, the Board of Trustees of St. Luke’s and Woman’s Hospitals decided to merge.
On January 1, 1953, the Woman’s Hospital became the Woman’s Hospital Division of St. Luke’s Hospital. The Board added “Center” to the Hospital’s name in the mid-1960s to acknowledge distinctions between the different Hospitals. The Woman’s Hospital Board of Governors merged with the corresponding board at St. Luke’s, but the Ladies Associate Board, which handled day-to-day business of the Hospital, continued to meet for some years.

Architect’s drawing of Woman’s Hospital Division
In 1979, St. Luke’s Hospital Center merged with the Roosevelt Hospital forming St. Luke’s-Roosevelt Hospital Center. In 1997, the Hospital Center joined with Beth Israel Medical Center under the Continuum Health Partners banner. In 2013, the Continuum Health Partners merged with Mount Sinai Medical Center forming the Mount Sinai Heath System. The Woman’s Hospital Division on St. Luke’s Hospital campus continued as such for a few years, but eventually duplicated services throughout the combined System. Services re-located, former names were changed, and Woman’s Hospital was consigned to history.
The Woman’s Hospital finding aid is available online here.




