Nov 24, 2020
Whenever you look back to the past, it is easy to find it all very strange, but a longer look allows us to see the threads that connect that time to this. Some of those threads are strong and enduring and others fray and end.
One of those strong threads that tie the Mount Sinai of 100 years ago to the Mount Sinai of 2020 is research and discovery. In 1920, Mount Sinai was dealing with the last wave of a deadly worldwide pandemic that had started in 1918 but still lingered. Some Mount Sinai physicians spent a great deal of time working on a “peculiar disease” that followed the epidemic. This was popularly called the ‘sleeping sickness,’ but doctors termed it epidemic encephalitis. Another Mount Sinai physician was lending his expertise as a member of a national commission that was established to deal with the ravages of empyema, which too often followed post-influenzal pneumonia. Other physicians were doing research on gastric diseases, leukemia, surgical innovations and cardiac problems – all topics that Sinai doctors continue to pursue.

Taken from 5th Ave. and 99th St. looking east over the new buildings. The building facing with the flag pole is the 1904 main building.
Another main theme from 100 years ago, as in every decade of Mount Sinai’s existence, was the physical changes being made on campus. The world war and epidemic had delayed the progress of the largest expansion plan ever envisioned by The Mount Sinai Hospital. First suggested in 1913, it was only in 1922 that all of the new buildings were completed and the renovations of older spaces finished. This resulted in a new Private Pavilion (our current Kravis Children’s Hospital), a new pediatric pavilion and pediatric clinic building, a larger employee dormitory, a larger laboratory building, and a new auditorium to accommodate Mount Sinai’s increasing educational efforts. The growth in the number of beds called for a larger house staff than before and allowed for the growth of new specialty services.
W hile these themes have echoes with our current year, as does the perennial nursing shortage of that era (among many others), there was much that was unique to Mount Sinai in 1920. In February of that year, Mount Sinai leaders held an event to celebrate the staff that had served in the World War I Mount Sinai affiliated unit, Base Hospital No. 3. Special commemorative medals were given to each veteran.
hile these themes have echoes with our current year, as does the perennial nursing shortage of that era (among many others), there was much that was unique to Mount Sinai in 1920. In February of that year, Mount Sinai leaders held an event to celebrate the staff that had served in the World War I Mount Sinai affiliated unit, Base Hospital No. 3. Special commemorative medals were given to each veteran.
The other topic of great interest in 1920 was the re-structuring of the medical staff to combine the in-patient and out-patient services under the in-patient chief of service. The Dispensary and the ward service had been two separate entities with limited overlap. The change allowed the clinic physicians to follow their patients when admitted to the hospital wards, and the ability to round and work with the in-patient staff made it more appealing to community physicians to take on clinic work. In the 1920 Annual Report, it was noted that the combined medical staff now numbered 250 physicians.
Certainly, times change. Institutions changes. Medicine changes. But even 100 years later, at Mount Sinai, some things never change.
Nov 9, 2020
I recently read a piece about Hamilton Square in the Roosevelt Island Historical Society’s From the Archives email. This park, which was named for Alexander Hamilton, existed on the Upper East Side of Manhattan from around 1807-1869. I found this fascinating since The Mount Sinai Hospital moved to Lexington Ave. and 66th St. in 1872. I knew that the City had ‘seeded’ this area with non-profit entities: Hunter College, many hospitals and schools, but I had never heard about the Square itself, which ran from 66th to 69th Streets between 3rd and 5th Avenues. Finally, Mount Sinai had a Hamilton connection, even though he died in 1804, 48 years before the Hospital was created!
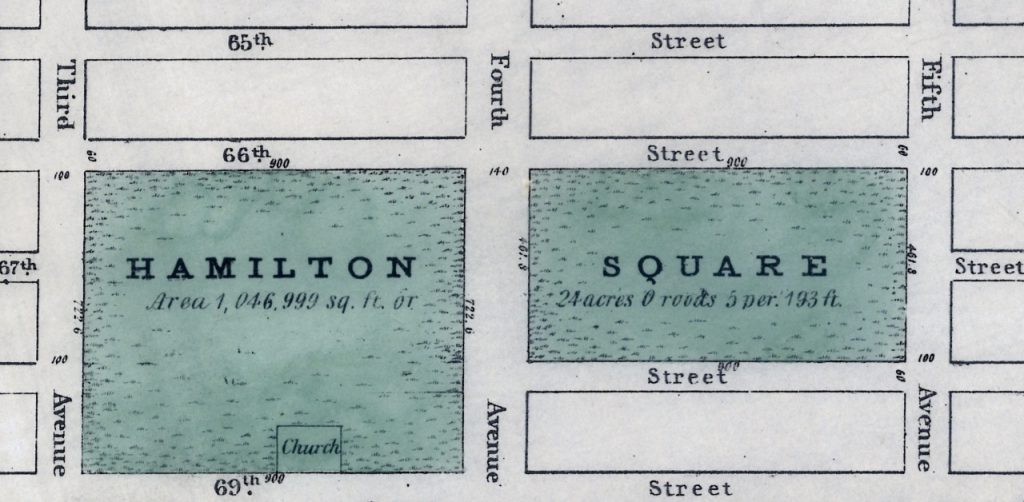
Map of Hamilton Square from the New-York Historical Society
When the Square was broken up, The Mount Sinai Hospital (MSH) was located on W. 28th Street, between 7th & 8th Avenues. It had been founded in 1852 as the Jews’ Hospital in the City of New York (the name was changed in 1866) and had opened its first building in 1855. After the Civil War, the leadership realized that the facility was inadequate and the location less than ideal due to the growth of the City. On November 2, 1867 the Directors authorized the purchase of ten lots of land from 65th to 66th Street on the west side of Park (then 4th) Ave. and later added eight more lots there. But then on October 6, 1868, the City leased Mount Sinai twelve lots of land between 66th and 67th on Lexington Ave. for $1 a year for 99 years. Somehow, over the interim, the City and Mount Sinai had reached an agreement on the Hospital taking over part of the former Hamilton Square. The earlier lots were later sold, saving Mount Sinai thousands of dollars. On May 25, 1870, the cornerstone for the second MSH was laid. The President of the Hospital, Benjamin Nathan, and Mayor Oakley Hall were there. (Within two months, Nathan was murdered in his bed on a ‘dark and stormy night.’)

On May 29, 1872, a dedication ceremony was held for the new Mount Sinai Hospital. When the building opened, it had a greatly expanded capacity of 110 beds. The building was designed by the well-known architect, Griffeth Thomas, and cost $335,000 to complete. It had an operating room in the basement of the north wards, rooms for our newly created House Staff to live in, a meeting room for the Directors, and a synagogue. Lexington Ave. remained unpaved for two more years, and the Hospital never wired the facility for electricity. A telephone was installed in 1882; the number was “Thirty-Ninth St., 257”. It was at this site that Mount Sinai transformed into what we would recognize as a modern hospital, with medical education and research joining its core mission of providing patient care.
In typical Mount Sinai fashion, this facility quickly became too small. Additional buildings were built and major renovations were begun in 1882. In 1890, Mount Sinai added a building across from the Hospital on the north side of 67th St. for our nursing school and Out Patient Department. This building is the only remnant of Mount Sinai that remains there today. It later served as the home of the Neurological Institute, the Polish legation, and finally became a school for the Archdiocese of NY. The Mount Sinai Hospital moved from Lexington Ave. in 1904 to its current East Side location on 100th St., between Madison and 5th Avenues. The name of Hamilton continues on various buildings and neighborhoods of the City, making its most recent appearance on Broadway.
Sep 25, 2020
Some of you may have read the sad story about the murder of a woman in the Justice Story column of the Daily News on Sunday. It is about how Irma Pradier thought she was going to run off with her boyfriend to California, but instead she was found murdered the next day along the Harlem Speedway, today known as the Harlem River Drive. I was particularly interested in this because it noted that she had been a maid at The Mount Sinai Hospital, and had even lived at the Hospital. I also realized that she had been hired before 1937, which meant there was a good chance the Aufses Archives had some record about her in our one existing employee logbook, which dates from 1882-1937. This lists all persons hired to work at Mount Sinai, which would exclude the medical staff who were generally not paid anything, or worked under a contract model.
And I was right!
Below is a portion of the page from our logbook that includes Irma Pradier. You can see from this she was hired February 13, 1934 and she lived ‘In,’ which would have meant the Employee Dormitory that faced 99th St., near Madison Ave. (across from today’s Atran and Berg buildings.) She was hired to be a Maid in the OPD (Out-Patient Department) for $35/month. (She would have also received a free meal as part of her compensation.) When she resigned on July 19, 1937, she had advanced to $47/month. As the News‘ article says, her reason for leaving is listed as “Going to Calif.” And the rest is history, or at least, an article in the Sunday Daily News.

The Irma Pradier entry from The Mount Sinai Hospital Employee Logbook
*The book is organized chronologically under each letter of the alphabet. Every entry was done by hand by an employee of the Personnel Office. This was THE official employment history of each worker. The blue bottom edge is from a long ago ink spill that saturated the pages. Note the other reasons for leaving employment. Some are fascinating!
Jul 6, 2020
This started out as a story about Althea Gibson, the first African American to win at Wimbledon, which she did on July 6, 1957. It was also about a summer sport, and being outside – two things people today find important and hopeful. But, as often happens in the Archives, those stories reminded us of other stories, which are, of course, about Mount Sinai.
In 1950, Harlem-born Althea Gibson made her U.S. Open debut at a time when tennis was largely segregated. On July 6, 1957, when she claimed the women’s singles tennis title, she became the first African American to win a championship at London’s All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club, aka Wimbledon. (Arthur Ashe was the first African American to win the men’s singles crown at Wimbledon in 1975. Ashe later had quadruple bypass surgery at St. Luke’s Hospital in 1979.) The Associated Press named Althea Gibson Female Athlete of the Year in 1957 and 1958. During the 1950’s, Gibson won 56 singles and doubles titles, including 11 major titles. Gibson retired from tennis and later became a professional golfer. She was voted into the National Lawn Tennis Association Hall of Fame in 1971 and died in 2003.

The Mount Sinai Hospital tennis courts on 5th Ave and 99th St, behind 5 E. 98th St., where KP is today.
Tennis has a long, up-and-down history at Mount Sinai. The first tennis court was built at the Hospital in the late 1800’s, back when the Hospital was still located at Lexington Avenue and 67th St. Space was tight, so the court was built between buildings, and the only way to get to it was to climb through a window on one of the wards. (Fortunately, a gong would sound whenever an Attending arrived at the Hospital, so the players were warned to get back inside.) In 1904, Mount Sinai moved uptown to 100th St., and it took 20 years before tennis returned. The growing House Staff asked the Trustees to build tennis courts that they could use for exercise. The Trustees

A small pewter trophy belonging to Noreen McGuire, School of Nursing Class of 1932. The trophy was for winning the tennis tournament in 1929.
eventually agreed in June 1923 and two courts were built on the southeast corner of 99th St and 5th Ave. Mount Sinai had purchased the land for future expansion needs, but had recently completed major additions to the campus and had no immediate plans to build. The courts were used by the Mount Sinai Hospital School of Nursing for gym classes, and nurses and doctors could sign up to play when a court was free.
The Aufses Archives has a wonderful interview with Gus Burton from 1988. Mr. Burton joined Mount Sinai’s staff in 1948, first as an x-ray file clerk, and then later trained as a technician in the Dept. of Radiology. What initially attracted him to work at Mount Sinai was because there was a tennis court. Here is how he described it:
Burton: …Back in those days the buses that ran along Fifth Avenue were owned by a company called the Fifth Avenue Bus Company. They had double deckers. The top deck was so that you could ride the bus for a nickel. At the time I was a student at NYU and sometimes I would take the bus down because the classes were at Washington Square. It was almost like a bus tour going down Fifth Avenue, seeing all the different places, and I saw the Hospital. I wasn’t impressed with the hospital so much, but where Klingenstein is there used to be tennis courts. At that time I was an avid tennis player, and I could see these people playing tennis. I thought it was very, very interesting, because I had found that there weren’t many places to play tennis in New York and here these people were running around playing tennis. Eventually, one day I was coming back home and I got off the bus. It was approaching the end of the semester and I said I need to find some kind of work for the summer. It was raining pretty hard, so I ran under the canopy that they had by the [Guggenheim] Pavilion. So I said, let me just check in here and see what’s going on. In those days, they didn’t really have what you call a personnel office. I guess they called it an employment office. They had about one or two clerks and the person who ran it, a Mr. Kerr (?). I just walked in and asked them if they had any jobs available. Said Mr. Kerr, “we may have some available in the radiology department. We’ll refer you to the person there who is looking for somebody and see what happens.”
So I went over and I was interviewed by a Dr. Joan Lipsay. She was the second in command in the radiology department. She was just really impressed that I came along and, sure, we’ll take you and they hired me as an X-ray file clerk. So I have always said in the years since then, that I had enough sense to come in out of the rain.
Interviewer: Did you ever get to play tennis?
Burton: Well, I found out after I started working here that those tennis courts were for the professional staff, the doctors and the nurses, and they were the ones I had seen playing on them. It so happened that one of the radiologists on our staff was an avid tennis player, he used to play out there frequently so I was able to get with him and I did get a chance to play on those tennis courts.
Unfortunately for Mr. Burton, the tennis courts were closed later in 1948, when Mount Sinai began the process of building the Klingenstein Pavilion along 5th Ave. It would be 65 years before tennis came back to Mount Sinai, but this time it was in a much different form. In 2013, it was announced that The Mount Sinai Medical Center was now the official medical services provider for the United States Tennis Association (USTA) and the U.S. Open. In addition, Alexis C. Colvin, MD, from the Leni and Peter W. May Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, would serve as the USTA’s Chief Medical Officer. In 2020, this continues to be the case. Every now and then, a mini-tennis court is built in the Guggenheim Pavilion lobby to showcase the Hospital’s role with the USTA, and for a brief moment, tennis is played again at Mount Sinai.
Jun 11, 2020
This is a continuation of a guest blog post by Colleen Stapleton. Colleen is a Patient Navigator with the Liver Education and Action Program (LEAP) at Mount Sinai, where she works to improve linkage to care for patients living with Hepatitis C. You can read the original post here.
Scanning
My first day scanning, the team and I addressed the technology involved in making our Mount Sinai News collection available online. I learned about the scanning specifications to best archive our newsletters digitally. These specifications included 300 dpi (dots per inch), “do not scale,” and others particular to our scanner.
I also learned how to navigate the interesting physical space of the IT office, where the scanner was placed in a small kitchenette. Since I was scanning during lunchtime, I saw a few lunches popped in and out of the microwave. I learned that I could go ahead and put the precious paper newsletters on a non-descript plastic yellow barrel drum object, but under no circumstances should papers be placed on the potentially wet nearby water cooler!
Starting with November of 1958, I began electronically piecing together our carefully preserved collection of Mount Sinai Hospital history.
Folding Paper
Gently unfolding each 60-odd year old newsprint was both a physical challenge and delight. I soon fell into the rhythm of scanning the first page, then the second, then switching to scanning the inserted third and fourth pages. Since the newsletters are not stapled, in total I would carefully reverse the seams of two folded pages, then finish up with the back section of the first folded page.
After a few sessions, I noticed that the newsletters were getting considerably longer – some included 12 pages! This 12-page spread would include a total of three seams, and so unfolding and folding would come to resemble the act of taking apart and putting back together a precious Russian doll.
Troubleshooting
My first day at the scanner I became aware that any file containing more than five pages could not be sent via email to our Archives team account. I made the decision at this time to scan four pages at a time, sending the files to the Archives account in pieces. I soon saw the stacks of newsletters flowing from the “un-scanned” to the “scanned” pile.
After each session I would return to my desk and make sure every issue was represented and the scan quality was good. The various parts of each issue were then virtually ‘stitched’ together. Though some months came and went without Mount Sinai Hospital News editions, each newsletter is marked chronologically with issue numbers.

The first Science News insert of the new Mount Sinai School of Medicine
One of my favorite developments in my scanning came with the advent of the Mount Sinai School of Medicine Science News, an insert that was developed as the medical school was founded and produced more and more significant scientific discoveries. There was also the Mount Sinai Medical Center News title change in November-December 1969 to correspond with the newly built school of medicine. The history of Mount Sinai was expanding before my eyes and I had to ensure my metadata reflected these changes!
Moving Forward with Metadata
After scanning part I of the MSH News archive, the team met with the Aufses Archives’ Digital Archivist to clarify our strategy moving forward. We confirmed our goal of making the Adobe PDFs of the News pages available online, creating a digital index of all MSH News electronic files, as well as providing readers with a search function powered by Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to more easily search the newsletter files.
We identified questions to the tune of “How should we put the PDF files online?” and “how can we most easily create an index to the publication?” We ultimately decided to OCR the PDF documents with Adobe and then dump the words into a database program used by the Aufses Archives called DBTextworks. We started with a few pilot issue files and we identified any necessary metadata fields for our project.
So began an exciting new phase: cleaning and inputting metadata. Unfortunately, this was interrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic and the need to stay home, and we have not been able to continue the scanning. However, the work continues with the efforts of a fantastic new summer intern working remotely — soon all of the scanned issues will be described and searchable.
Stay tuned for more blog installments exploring this digitization project along with coverage of the many unique historical Sinai snapshots found in the MSH News!

 hile these themes have echoes with our current year, as does the perennial nursing shortage of that era (among many others), there was much that was unique to Mount Sinai in 1920. In February of that year, Mount Sinai leaders held an event to celebrate the staff that had served in the World War I Mount Sinai affiliated unit, Base Hospital No. 3. Special commemorative medals were given to each veteran.
hile these themes have echoes with our current year, as does the perennial nursing shortage of that era (among many others), there was much that was unique to Mount Sinai in 1920. In February of that year, Mount Sinai leaders held an event to celebrate the staff that had served in the World War I Mount Sinai affiliated unit, Base Hospital No. 3. Special commemorative medals were given to each veteran.





